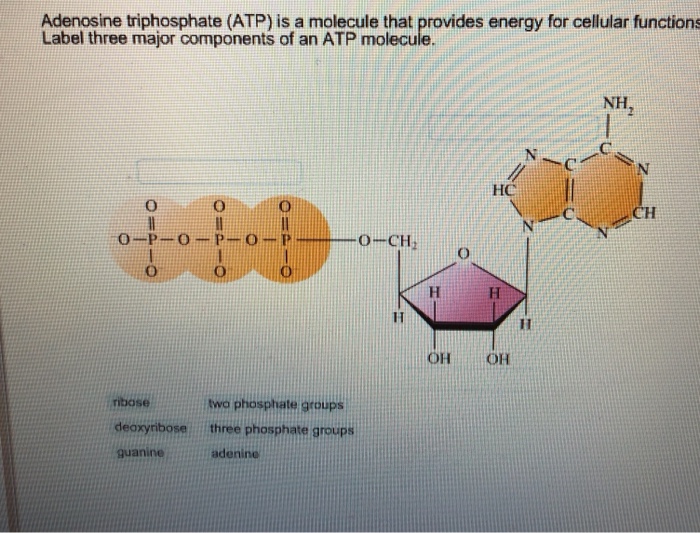
41 label the atp molecule
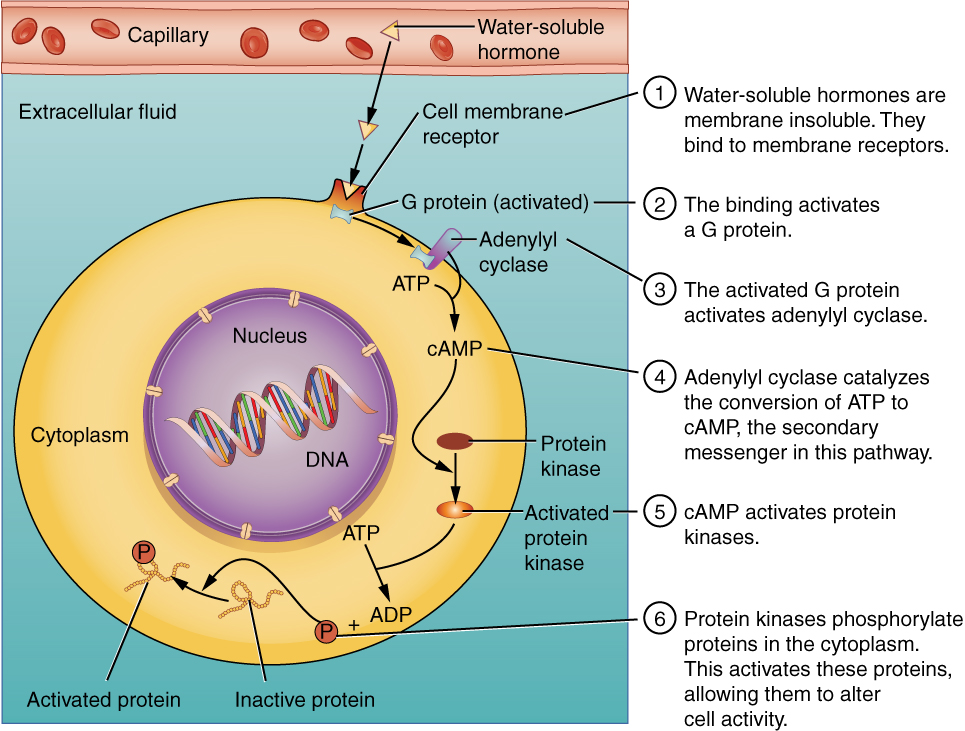
Screenshot_20220526-081745~2.png - Part 3: ATP Synthesis ATP molecules ... Is the ENTIRE energy molecule called ATP or ADP? Be sure to LABEL the name below! ENERGY Absorbed Part 4: The ATP-ADP Cycle ATP decomposition (part 2) and ATP synthesis (part 3) are the processes in the ATP-ADP Cycle. Using what you learned in the above activities, complete the diagram below (use the word bank as a guide) and summarize in not ... DP Biology: Membrane transport models - ThinkIB Membrane transport models. Using all that we know about molecules and about the structure of the cell membranes students are challenged to illustrate the transport of four very different molecules through the membrane using play-doh, spaghetti, food and sweets. Protein pumps, protein channels, and the phospholipid bilayer are central to the story.
MCQ on ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) - YB Study The ATP molecule contains five elements C, H, O, N, and P. T stands for thymine, so the structure of ATP is very similar to that of nucleotides D. When 1 mole of ATP is hydrolyzed, the released energy of 30.54kJ is stored in two high-energy phosphate bonds Answer: B 16. Which of the following statements about ATP in human cells is correct________
Label the atp molecule
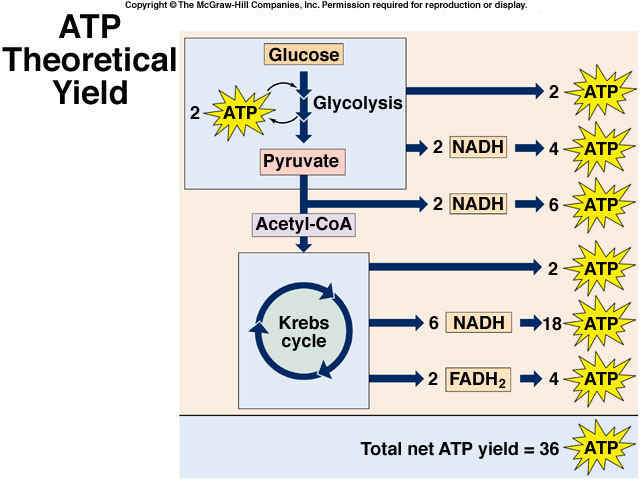
LAB 6 Fermentation & Cellular Respiration While 2 ATP per glucose molecule is clearly better than nothing, it is not nearly enough to meet the energy needs of complex multicellular organisms such as plants and animals. To get the maximum ATP yield from molecules of glucose requires cellular respiration, which and produce up to 36 ATP per glucose molecule. In aerobic organisms, cellular respiration requires O 2 … ATP synthesis and storage - PMC 12.04.2012 · ATP is universally seen as the energy exchange factor that connects anabolism and catabolism but also fuels processes such as motile contraction, phosphorylations, and active transport. It is also a signalling molecule in the purinergic signalling mechanisms. In this review, we will discuss all the main mechanisms of ATP production linked to ... 4-Amino-TEMPO, free radical 97 14691-88-4 - Sigma-Aldrich Each actin molecule contains a nucleotide, tightly bound in a deep cleft that divides the molecule. To probe conformational changes within this region of the molecule, we have incorporated two spin label analogues of ATP into actin. In both analogs Spin-Labeled Dendrimers in EPR Imaging with Low Molecular Weight Nitroxides.
Label the atp molecule. 2019 Biology Written examination - Pages 2019 BIOLOGY EXAM 6 SECTION A – continued DO NOT WRITE IN THIS AREA Question 14 In glycolysis, the ATP yield per molecule of glucose is A. 4 ATP produced and 2 ATP used for a net gain of 2 ATP. B. 2 ATP produced and 4 ATP used for a net loss of 2 ATP. C. 36 to 38 ATP produced for a net gain of 2 ATP. D. 36 to 38 ATP used for a net loss of 2 ATP. Question 15 … Insights into the client protein release mechanism of the ATP ... 20.05.2022 · How ATP-independent chaperones release their clients without energy input remains enigmatic. Here the authors discover that chaperone Spy uses its long, disordered N terminus to facilitate client ... EOF Bio Final Exam Study Guide Flashcards | Quizlet soluble in water. Protein function. is determined by interaction of surface R groups with other molecules. When amino acids link together to form a polypeptide, the peptide bonds that form are between. an amino group and a carboxyl group. Starch and glycogen, which are both polysaccharides, differ in that starch _______, while glycogen _______.
Biology Test - June 7 2022 Flashcards | Quizlet What is ATP used for? To release and store energy Label an ATP Diagram Middle (Single octagon - Ribose) Side (three circles - Phosphate) Side (Two octagons merged together - Adenine) What is the purpose of the ATP cycle? ATP transfers energy from the breakdown of food molecules (cellular respiration) to power the cell functions.; energy source ATP hydrolysis coordinates the activities of two motors in a dimeric ... Introduction. ATP-dependent chromatin remodelers are enzymes that restructure eukaryotic genomes in order to facilitate all DNA-based processes, including transcription, DNA damage repair, and replication (, , ).Their substrates are chromatin, the protein-nucleic acid complex that stores a cell's genetic information, and in particular the nucleosome, the basic repeating unit of chromatin ... Magnesium in biology - Wikipedia Magnesium is an essential element in biological systems.Magnesium occurs typically as the Mg 2+ ion. It is an essential mineral nutrient (i.e., element) for life and is present in every cell type in every organism. For example, ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the main source of energy in cells, must bind to a magnesium ion in order to be biologically active. Ribose - Wikipedia Ribose is a simple sugar and carbohydrate with molecular formula C 5 H 10 O 5 and the linear-form composition H−(C=O)−(CHOH) 4 −H. The naturally-occurring form, d-ribose, is a component of the ribonucleotides from which RNA is built, and so this compound is necessary for coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes.It has a structural analog, deoxyribose, which is …
Oxidative phosphorylation - Wikipedia Oxidative phosphorylation (UK / ɒ k ˈ s ɪ d. ə. t ɪ v /, US / ˈ ɑː k. s ɪ ˌ d eɪ. t ɪ v /) or electron transport-linked phosphorylation or terminal oxidation is the metabolic pathway in which cells use enzymes to oxidize nutrients, thereby releasing chemical energy in order to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In eukaryotes, this takes place inside mitochondria. ... Sawyer-KKerr The other label is an organic quencher molecule. If a cell needs to spend energy to accomplish a task the ATP molecule splits off one of its three phosphates becoming ADP Adenosine di-phosphate phosphate. When a phosphate group breaks off from another this is formed. A single ATP molecule is made up of three parts adenine ribose and phosphates. Skeletal muscle tissue: Histology - Kenhub Myosin hydrolyses ATP to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and a phosphate molecule. This provides energy needed for the myosin head to rotate to a 90° angle and reattach to a new actin. Power stroke - When the muscle is not contracting, the myosin binding site is partially blocked by a troponin molecule. During contraction calcium binds to troponin ... Formation Of ATP: Meaning, Respiration, and Photosynthesis Formation of ATP: Adenosine triphosphate, or ATP, is the primary molecule at the cellular level that stores energy for future reactions or allows the cell to withdraw energy to carry out reactions during times of need. Through the breakdown of food, organisms obtain energy that is stored as ATP.
MCQ on Translation (Protein Synthesis) - YB Study A. One molecule of GTP. B. One molecule of ATP. C. Two molecules of GTP. D. Two molecules of ATP. Answer: A. 6. What are codons in genetics_____ A. 3 adjacent bases on a DNA strand. B. 3 adjacent bases in mRNA that determine an amino acid. C. 3 bases at one end of the tRNA. D. 3 adjacent base pairs on a DNA molecule. Answer: B. 7.
Actin Assembly (Theory) - Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham In the F filaments, since all the actin monomers are oriented in the same direction, actin filaments have a distiEach actin molecule contains a Mg2+ ion complexed with either ATP or ADP. Thus there are four states of actin: ADP - G-actin, ATP - G-actin, ADP - F-actin, and ATP - F-actin.
Eccentric muscle contraction: Examples - Kenhub According to this theory, the myosin heads cyclically attach to specific sites on actin filaments, forming cross-bridges. Each cross-bridging cycle consumes one molecule of adenosine triphosphate, or ATP (energy). Once attached, the myosin heads pull the actin filaments and cause the myofibrils to slide past each other.
Glycolysis - Wikipedia Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose (C 6 H 12 O 6), into pyruvic acid (CH 3 COCO 2 H).The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy molecules adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH). Glycolysis is a sequence of ten reactions catalyzed by enzymes.
PharmaCircle This website uses cookies to help provide you with the best possible online experience. Please read our Terms & Conditions and Privacy Policy for information about ...
Phosphate Backbone - Genome.gov A phosphate backbone is the portion of the DNA double helix that provides structural support to the molecule. DNA consists of two strands that wind around each other like a twisted ladder. Each strand has a backbone made of alternating sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate groups. Attached to each sugar is one of four bases--adenine (A), cytosine ...
Nucleotide - National Human Genome Research Institute Home A nucleotide is the basic building block of nucleic acids (RNA and DNA). A nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule (either ribose in RNA or deoxyribose in DNA) attached to a phosphate group and a nitrogen-containing base. The bases used in DNA are adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) and thymine (T). In RNA, the base uracil (U) takes the ...
Fluorescence Polarization Assays in Small Molecule Screening Using this setup, small molecule inhibitors of PPIs can potentially be identified when high FP value is retained upon addition of protein B in the presence of inhibitor (i.e., the potential inhibitor prevents protein B from binding to protein A and from displacing the labeled aptamer). Such an approach may be limited to the identification of allosteric inhibitors of protein A or inhibitors ...
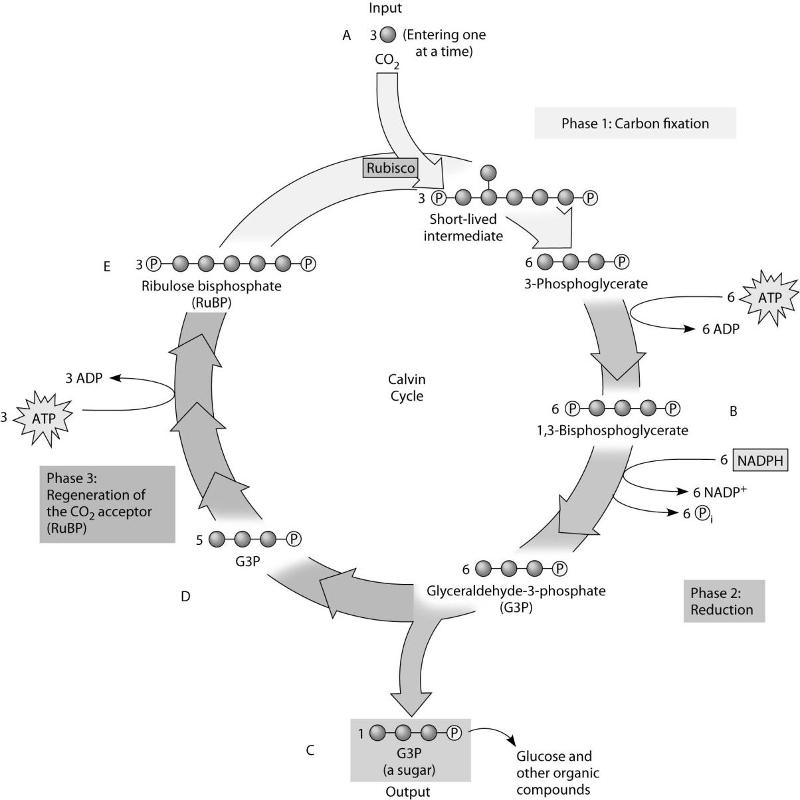
Photosynthesis Flashcards | Quizlet Label diagram 7 with three phases of the Calvin cycle. Phase 1: Fixation Phase 2: Reduction Phase 3: Regeneration (Diagram 8) Phase 1, Description . In organic carbon, in the form of carbon dioxide from the air, is incorporated into organic molecules, a process known as carbon fixation. (Diagram 8) Phase 1, What enzyme catalyzes the reaction in this phase? The enzyme …



Post a Comment for "41 label the atp molecule"