43 label of nucleotide
Bisulfite sequencing - Wikipedia Bisulfite sequencing (also known as bisulphite sequencing) is the use of bisulfite treatment of DNA before routine sequencing to determine the pattern of methylation. DNA methylation was the first discovered epigenetic mark, and remains the most studied. In animals it predominantly involves the addition of a methyl group to the carbon-5 position of cytosine residues of the … Nucleotides | Types, Examples, Functions & Classification Nucleotides perform several important functions in the human body in free state as well as a component of nucleic acids. For example, ATP is a nucleotide that acts as energy currency of a cell. GDP and GTP are nucleotides essential for cell signaling. NAD is a dinucleotide that acts as a coenzyme in various metabolic reactions.
ADRIAMYCIN (DOXOrubicin HCl) for Injection Intercalation inhibits nucleotide replication and action of DNA and RNA polymerases. The interaction of doxorubicin with topoisomerase II to form DNA-cleavable complexes appears to be an important mechanism of doxorubicin cytocidal activity. Doxorubicin cellular membrane binding may affect a variety of cellular functions. Enzymatic electron reduction of doxorubicin by a …

Label of nucleotide
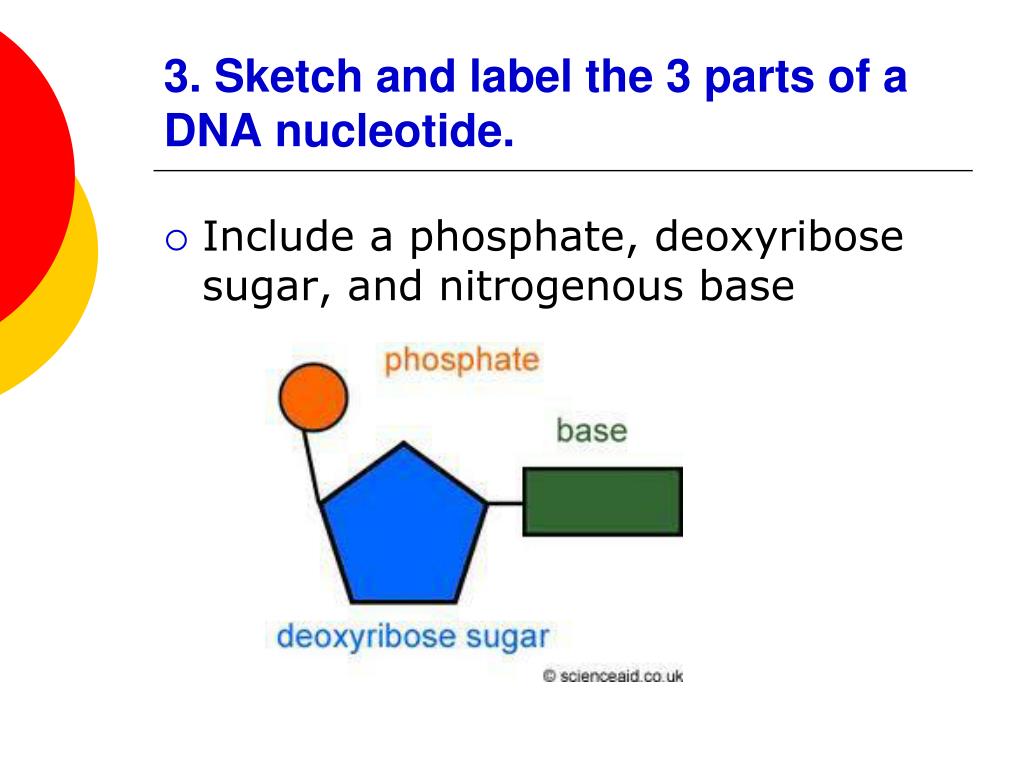
Nucleotides in DNA | Science Primer Nucleotide Nucleoside. DNA is a nucleotide polymer, or polynucleotide. Each nucleotide contains three components: A five carbon sugar. A phosphate molecule. A nitrogen-containing base. The sugar carbon atoms are numbered 1 to 5. The nitrogenous base attaches to base 1, and the phosphate group attaches to base 5. What are the Three Parts of a Nucleotide? | Albert.io Figure 2: The chemical assembly of the three parts of the nucleotide, the phosphate (blue box), nitrogenous base (red box) and the pentose sugar. This particular nucleotide is adenine. The assembly of nucleotides (1) differentiates them from nucleosides, which do not contain a phosphate group (in the blue box); (2) allows the nucleotide to ... DNA Structure - YouTube Learn about the structure of DNA and how to recognize all the parts in this video!
Label of nucleotide. Genetic Linkage - University of Utah To see how linkage works, let's look at some specific genes. Two of the genes (1 and 2) are relatively far apart (top illustration). Each gene comes in two different versions, or alleles: A and B. Nucleotide: Structure, Examples and Function - BYJUS A nucleotide consists of three units, which are covalently linked. They are: 1. Nitrogenous Base: They contain purine or pyrimidine base. DNA contains adenine (A), guanine (G), thymine (T) and cytosine (C), whereas RNA contains adenine, guanine, uracil (U) and cytosine. 2. Sugar: A nucleotide contains a pentose sugar. How (and Why) to Label Nucleic Acids - Bitesize Bio Generally speaking, there are two types of nucleic acid labeling techniques: radioisotope labeling and non-radioactive labeling. Radioisotope labeling: Considered as a conventional method for nucleic acid labeling, radiolabeled nucleotides are synthesized using ATP-gamma- 32 P or 35 P. They are easily incorporated into nucleic acid sequences by ... Building Blocks of Nucleic Acids | Structures & Functions Importance of Nucleotides. As building blocks of nucleic acids, nucleotides primarily aid in storing genetic information that will be later the basis for the manifestation of physical traits. Moreover, they also play roles in various biological and physiological processes. As molecules, they help in the transport of ATP and serve as biological ...
Nucleotides labeled with... - Jena Bioscience Nucleotides by Structure Nucleotides labeled with... All Products. Nucleotides & Nucleosides. Nucleotides by Structure A nucleotide-sensing oligomerization mechanism that controls … 16.05.2022 · Ribonucleotide reductase (RNR) is an essential enzyme that catalyzes the synthesis of DNA building blocks. Here, the authors present the cryo-EM structure and mechanism of action of NrdR, the RNR ... What Is a Nucleotide? Definition, Structure, and Function Each nucleotide is a molecule, so while the bases are extremely important for how the nucleotide is classified and for its eventual function, they cannot form without the other elements that make up the molecule. One of these elements is simple, five-carbohydrate sugars. A nucleotide can contain one of two sugars: Deoxyribose, a monomer of DNA, OR Labeling Oligonucleotides and Nucleic Acids—Section 8.2 Structures of the ChromaTide Nucleotides. The ChromaTide UTP and dUTP nucleotides are modified at the C-5 position of UTP or dUTP via a unique aminoalkynyl linker (Figure 8.2.2).The C-5 position of UTP and dUTP is not involved in Watson-Crick base-pairing and so interferes little with probe hybridization.The aminoalkynyl linker between the fluorophore and the nucleotide in the ChromaTide UTP ...
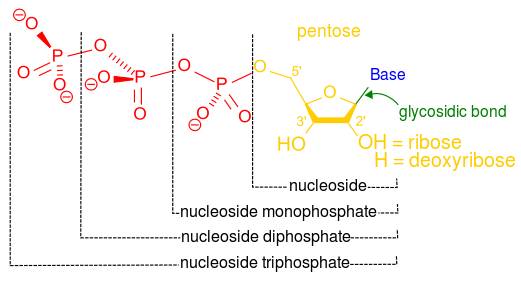
Methods for Labeling Nucleic Acids - Thermo Fisher Scientific Because these methods label at random sites along the length of a DNA or RNA molecule, they allow a higher degree of labeling to be achieved than end-labeling techniques. However, one disadvantage of these methods is that the nucleotide bases are directly modified, which will reduce or prevent base-pairing between complementary strands during ... PDF nucleoside nucleotides - Vanderbilt University nucleotide units in nucleic acids is a phosphodiester, which connects the 5'-hydroxyl group of one nucleotide to the 3'-hydroxyl group of the next nucleotide. By convention, nucleic acid sequences are written from left to right, from the 5'-end to the 3'-end. Nucleic acids are negatively charged 28.7: Nucleic Acids. The 5 Kinds of Nucleotides - ThoughtCo The five bases are adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine, and uracil, which have the symbols A, G, C, T, and U, respectively. The name of the base is generally used as the name of the nucleotide, although this is technically incorrect. The bases combine with the sugar to make the nucleotides adenosine, guanosine, cytidine, thymidine, and uridine. Nucleotide symbols - Cardiff University Nucleotide symbol: Full Name: A: Adenine: C: Cytosine: G: Guanine: T: Thymine: U: Uracil: R: Guanine / Adenine (purine) Y: Cytosine / Thymine (pyrimidine) K: Guanine ...
Nucleotide labeled structure Diagram | Quizlet Start studying Nucleotide labeled structure. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
(GEMCITABINE HCl) FOR INJECTION gemcitabine nucleotide is incorporated into DNA, only one additional nucleotide is added to the growing DNA strands. After this addition, there is inhibition of further DNA synthesis. DNA polymerase epsilon is unable to remove the gemcitabine nucleotide and repair the growing DNA strands (masked chain termination). In CEM T lymphoblastoid cells ...
The Structure of DNA The Structure of DNA. This figure is a diagram of a short stretch of a DNA molecule which is unwound and flattened for clarity. The boxed area at the lower left encloses one nucleotide. Each nucleotide is itself make of three subunits: A phosphate group (a phosphorous atom surrounded by four oxygen atoms.) (Labeled P) And one of four nitrogen ...
Nucleotide and Structural Label Identification in Single RNA Molecules ... Here we present a method for direct nucleotide identification and structural label mapping of single RNA molecules via Quantum Molecular Sequencing (QMSeq). The method combines non-perturbative quantum tunneling spectroscopy to probe the molecular orbitals of ribonucleotides, new experimental biophysical parameters that fingerprint these ...
Labeled Nucleotides - Biotium Nucleotide analogs and nucleotides labeled with biotin or fluorescent dyes. dCTP and dUTP are available conjugated to our bright and photostable CF® Dyes, in a variety of colors. ... The CF® dye TUNEL Assay Apoptosis Detection Kit label apoptotic cells in fixed tissue sections or cellular samples for fluorescence microscopy or flow cytometry ...
How do you draw a nucleotide and label its three basic parts? Explanation: The above structure is a nucleotide. It consists of a: phosphate group. 5-carbon sugar, and. nitrogenous base.
Nucleotide - Wikipedia A nucleotide is composed of three distinctive chemical sub-units: a five-carbon sugar molecule, a nucleobase—the two of which together are called a nucleoside—and one phosphate group.With all three joined, a nucleotide is also termed a "nucleoside monophosphate", "nucleoside diphosphate" or "nucleoside triphosphate", depending on how many phosphates make up the phosphate group.
Label/quencher-free detection of single-nucleotide changes in DNA using ... This system is a label/quencher-free fluorescence enhancement system based on rolling circle amplification (RCA)-responsive G-q … Label/quencher-free detection of single-nucleotide changes in DNA using isothermal amplification and G-quadruplexes Analyst. 2016 Nov 28;141(24):6503-6506. doi: 10.1039/c6an01600f. Authors Il Joon Lee 1 ...
BankIt Submission Help: Feature Table File The first line of the feature table contains the following basic information >Feature Sequence_ID The sequence identifier (Sequence_ID) must match the label used to identify each table's corresponding sequence in the nucleotide FASTA file. Subsequent lines of the table list the features. Prepare the feature table file in a text editor and save it as plain ascii text (not .rtf or …




Post a Comment for "43 label of nucleotide"