41 moss structure diagram
Life cycle - Sporophyte development - moss - bryophyte There's more than spores to a spore capsule and the internal structure can vary from species to species. The diagram (right) gives a cut-away view of a spore capsule of the moss Funaria hygrometrica, a cosmopolitan species that features commonly in structural or physiological studies. At the bottom of the diagram you can see part of the seta. moss | Definition, Characteristics, Species, Types, & Facts The stemlike and leaflike structures of moss plants constitute the gametophytic (sexual) generation. The sporophytic (asexual) generation develops from the gametophyte and usually consists of a raised stalk, or seta, which terminates in the sporangium. The sporangium remains dependent on the gametophyte, to varying degrees, for water and nutrients.
Chemical structure of peat-moss | Download Scientific Diagram Fig 1 illustrates the chemical structure of peat-moss [13]. After heating a biosorbent, decrease in the sorbent mass due to loss of humidity was noticed. Sorbent mass losses at heating temperatures...
Moss structure diagram
Mosses - Brian McCauley Moss body structure Mosses are often leafy, but they lack the complex organization of vascular plant leaves, stems, and roots. A cross section of the leaf shows that most of it is only one cell thick. There is no epidermis, no cuticle, and there are no stomata. All the cells are lined with chloroplasts. Quick Notes on Sphagnum (With Diagram) | Biology In some species of Sphagnum for e.g., S. molluscum, S. tenellum, some cortical cells elongate to form a long curved structure with a curved neck and an opening. These modified cells resemble a retort hence; these cells are called 'retort cells' (Fig. 6A, B). There cells are inhabited by small microscopic animals. PDF Morphology of Mosses (Phylum Bryophyta) - eFloras.org The fundamental moss leaf consists of a unistratose lamina and a multistratose costa or midrib (Fig. 3). However, in a few families, the entire leaf is multistratose, and in many others, leaf margins are multistratose, or otherwise differentiated from the rest of the lamina (Fig. 4).
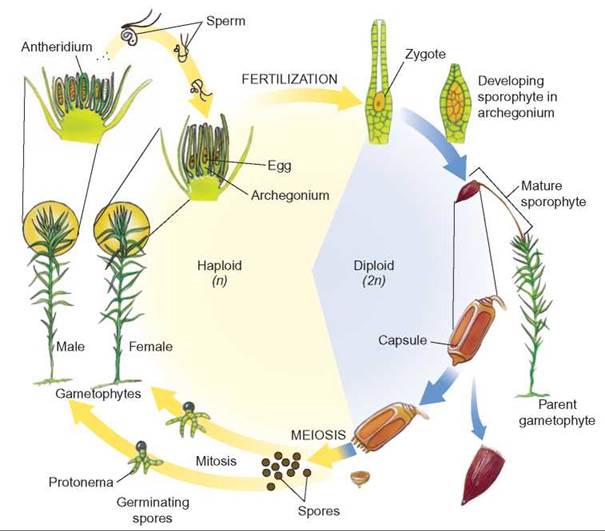
Moss structure diagram. How can I export moss structure to visio diagram Hello, I would like to have in visio, the whole diagram of the structure of the sharepoint. For ex. which content types include which site columns or other content types and which lists have which content types or which lookup fields from which lists, etc. Is there a program that does that ... · I guess there is nothing available Out of Box. Have you ... The Moss Life Cycle | Moss Gametophyte, Reproduction Parts & Diagram ... Moss life cycle diagram: the red boxes show the male antherdial part while the blue boxes show the female archegonial part, both are required for sexual reproduction. Both of the mature... What is Moss? | Characteristics, Facts, Examples, Structure ... Learn the definition of moss, moss as a plant, and physical characteristics of mosses, classification of mosses, structure and root system. Updated: 10/28/2021 Table of Contents PDF Lab 12: Bryophytes : Mosses and Liverworts (and hornworts) Mosses: Class Bryophyta • Gametophytes are leafy. • Sporophytes have capsules on the end of stalks (setae). Thalloid liverworts: Class Marchantiophyta • Flat thallus • Umbrella-shaped structure on gametophyte is a carpocephalum. • Sporophyte is hidden under the carpocephallum.
Moss - Wikipedia Moss gametophytes have stems which may be simple or branched and upright or prostrate. Their leaves are simple, usually only a single layer of cells with no internal air spaces, often with thicker midribs. They do not have proper roots, but have threadlike rhizoids that anchor them to their substrate. How does moss reproduce? The life-cycle of moss Inside the capsule can be anywhere from 4 to over a million spores depending on the species of moss. On the front of the pod capsule are a set of 'teeth' called the ' peristome ' that controls the release of the spores. The front of the capsule has a set of teeth closed together. Structure of a moss leaf - Mosses - Te Ara Structure of a moss leaf Next Most moss leaves are very simple and consist of a single layer of photosynthetic cells. Water and gases from outside pass easily into the cells. This moss, Distichophyllum kraussei, has elongated cells on its leaf margin and a central thickening, known as a nerve, that supports the leaf. Using this item labelled diagram of Sporophyte of Moss - QS Study The following parts are found in the longitudinal section of the moss capsule. (i) Apophyses, (ii) Capsule wall, (iii) Air cavity, (iv) Sporangium, (v) Columella, (vi) Operculum, (vii) Annulus & (viii) Peristome. Apophyses: The swollen part at the attachment of the capsule and seta is called apophyses.
Data table 4 moss structure images plant part - Course Hero Moss Structure Images. Plant Part Structure (Viewed with Hand Lens) Structure (Viewed with Microscope) Gametophyte Sporangium Sporophyte Rhizoid Leaf-like Structure Antheridium Archegonium Questions A. When visualizing moss, a low-lying soft green plant may come to mind. Would this visualization reflect the gametophyte, sporophyte, or rhizoid? B. Draw a Labelled Diagram of Gametophyte of Moss - QS Study They are slender, branched, and multicellular and have oblique septa. They arise from the base of the axis. Rhizoids instead of roots, fix the plant firmly with the soil and absorb water and mineral. Mosses are bryophytes and have no proper stem or roots. It has two parts sporophyte and gametophyte. Mosses | Basic Biology Mosses. Mosses are a phylum of non-vascular plants. They produce spores for reproduction instead of seeds and don't grow flowers, wood or true roots. Instead of roots, all species of moss have rhizoids. The mosses sit within a division of plants called the Bryophyta under the sub-division Musci. Life Cycle of a Moss - Infographic - STEM Lounge A tiny tooth-like structure around the mouth of the capsule controls the release of the spores. These structures, called the peristome, consist of one or two rows of teeth. They prevent the release of the spores during wet conditions by remaining closed. In dry conditions they open, releasing the spores.
Garden Guides | Parts of a Moss Plant The capsule consists of the base (urn) and a lid (operculum), and inside are the peristome, which resemble two rows of tiny teeth. The peristome help keep the spores inside until they are mature and ready to be distributed. Mosses do not produce flowers or seeds and instead reproduce with spores, like fungi or ferns.
Moss: Definition, Examples, Types and Life Cycle - Biology Dictionary This is the dominant structure of moss, what you typically see if the moss is not reproducing. This can be seen in the image at the base of the sporophyte, much shorter and seemingly a different species. The gametophyte is responsible for producing gametes, which are capable of fusing together. Look at the image below, of moss reproduction.
PLANTS & GARDENING :: PLANTS :: MOSS :: STRUCTURE OF A MOSS image ... rhizoid Rootlike filament enabling the moss to anchor itself to its substrate and absorb water and mineral salts. stem Main part of the moss from which the leaves spiral outward; it can be upright or flat. leaf Part of the moss originating at the stem, especially adapted to capture light, perform photosynthesis and absorb water. photosynthesis
Mosses (phylum Bryophyta) - bryophyte The accompanying diagram shows a cross section of a leaf of the species Aloina rigida. The central brown section, several cells thick, is the nerve. On each side of the nerve the leaf is just one cell thick and is curved inwards. Each green "pillar" indicates one lamella.
Solved Label the structures on this diagram of a moss. Drag - Chegg Drag | Chegg.com. Science. Biology. Biology questions and answers. Label the structures on this diagram of a moss. Drag the labels onto the diagram below. Not all labels will be used. Question: Label the structures on this diagram of a moss. Drag the labels onto the diagram below.
Draw a diagram to describe the life cycle of the moss, pointing out ... Solution. The life cycle of most mosses begins with the release of spores from a capsule, which opens when a small, lidlike structure, called the operculum, degenerates. A single spore germinates to form a branched, filamentous protonema, from which a leafy gametophyte develops. The gametophyte bears organs for sexual reproduction.
Moss Antheridia - Florida State University Moss Antheridia. Reproduction of mosses, an advanced group of the green seedless plants known as Bryophytes, may take many forms. New plants may develop through branching, fragmentation, regeneration, or production of spores. In the gametophyte form of mosses, reproduction is generally sexual and is seasonally controlled.
Moss Diagram: Biology | Biology plants, Evolution of plants, Plant science The familiar leafy moss plant is the sexual phase of the moss life cycle. When mature, most mosses develop sex organs . Some mosses have separate male and female plants, whereas others have male and female sex organs on the same plant. In wet conditions, sperm cells are released from male sex ...
PDF Morphology of Mosses (Phylum Bryophyta) - eFloras.org The fundamental moss leaf consists of a unistratose lamina and a multistratose costa or midrib (Fig. 3). However, in a few families, the entire leaf is multistratose, and in many others, leaf margins are multistratose, or otherwise differentiated from the rest of the lamina (Fig. 4).



Post a Comment for "41 moss structure diagram"